Just imagine you are playing an online game and it keeps stuttering. Or you are trying to stream your favorite tv show and it keeps pausing. How frustrating and irritating it is. Ever wondered why does this happen?
Well, it is all thanks to packet loss. So, what is packet loss? And how do you fix it, you may ask.
Here is everything you need to know about packet loss.
What is Packet Loss?
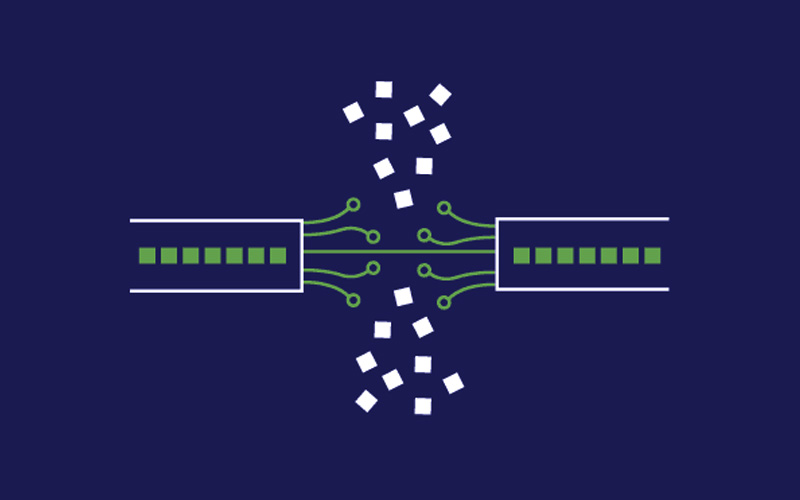
Before you know more about packet loss, you must know about the packet. Data you send over the internet is known as a packet. Videos, emails, and voice communication are packets. When you send a packet, it will take the most efficient way to reach its destination.
Sometimes, the packet or information fails to reach the intended destination. Such errors mostly occur when the information has traveled far. So, packet loss is when the packet gets lost in transit. Lost packets cause several problems like bottlenecks, slow down the network speed, and decrease the network bandwidth and throughput.
Moreover, packet loss can prove to be quite expensive. In case you don’t reduce packet loss in your system, you will have to spend a lot of money on updating your IT infrastructure.
What Causes Packet Loss?
There are many causes of packet loss. Here are some of the most common causes.
Network Congestion
We all know that information goes through several links and devices. When these links hit maximum capacity, a queue is formed that slows down the process of passing information. That is a general problem in which information often gets left behind.
Faulty Hardware
Another reason that causes packet loss is damaged hardware such as routers, cables, modems, and corrupt network card drivers. These things can lead to packet loss. Also, in large companies, firewalls and network switches can lead to packet loss.
Wireless Network is Unreliable
Since everything is connected through Wi-Fi, this increases the chance of packet vanishing. That is because wireless networks are open to a wide range of unpredictable elements like radio frequency, other wireless networks, distance, and thick walls.
How to Fix Packet Loss?
Though there are many causes of packet loss, you can give these solutions a try.
Restart Your Computer
One of the ways to fix this problem is by restarting your computer. It is possible that you might be running software on your computer that causes problems. For instance, Google Chrome is a heavy application and it consumes 75% of memory. It results in other applications or services to crash. The problem can be resolved by restarting.
Update Your Software
We know how annoying software updates can be. However, updates are crucial for the smooth operation of the software. That is because the older firmware might have flaws that cause packet loss.
Hence, it is important to make sure the software is up to date.
Check the Internet Connection
It is no rocket science. Sometimes, the cables are not plugged in and it leads to all types of problems. So, you can check the cable to make sure it is not causing any problem.
If you have a wired connection, you can unplug it and plug it again. In case you have a wireless connection, check the connection of your router.
Get Rid of Things Leading to Static
Sometimes devices like wireless speakers, cameras, headphones, and Bluetooth devices might cause static. These things can interfere with the path that leads to several issues. By eliminating these, you can fix the problem of packet loss.
Give Cabled Connections a Try
It is no surprise the use of Wi-Fi is increasing every day. Everything is connected through Wi-Fi; this makes it easy for a packet to go missing. If you use ethernet rather than Wi-Fi, you can ensure the information reaches its destination.
We hope these solutions will help fix the problem. If you still encounter the problem, you can use tools to reduce packet loss.
FAQs
Yes, it is one of the reasons for packet loss.
Of course, there are many tools available on the internet that you can use. But the above-mentioned steps will resolve the problem.
Well, yes, if the hardware is causing problems, replacing it can help fix the problem.
There are plenty of reasons for it.
– Problems with hardware
– Network congestion
– Software bugs
– Security threats
– Overburdened devices.